Toyota Sienna 2010-2026 Owners Manual: Active head restraints
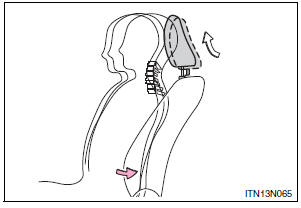
When the occupantŌĆÖs lower back presses against the seatback during a rear-end collision, the head restraint moves slightly forward and upward to help reduce the risk of whiplash on the seat occupant
Active head restraints
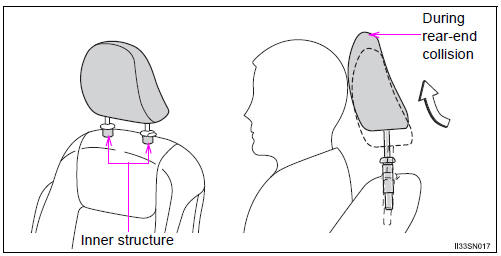
Even small forces applied to the seatback may cause the head restraint to move. When a locked head restraint is pushed up forcibly, the head restraint inner structure may appear. This does not indicate a problem.
| WARNING When adjusting the seat position
Seat adjustment
|
 Adjustment procedure
Adjustment procedure
Manual seat
Seat position adjustment lever
Seatback angle adjustment lever
Vertical height adjustment lever (driverŌĆÖs side only)
Lumbar support adjustment switch (driverŌĆÖs side ...
 Rear seats
Rear seats
...
Other materials:
Disassembly
1. REMOVE TRANSFER COVER GASKET
(a) Remove the transfer gasket from the transfer
assembly.
2. REMOVE TRANSFER CASE BREATHER PLUG
(a) Using a screwdriver and a hammer, remove the
transfer case breather plug from the No. 1 transfer
case cover.
NOTICE:
Be careful not to damage the conta ...
Skid Control ECU Communication Stop Mode
DESCRIPTION
Detection Item
Symptom
Trouble Area
Skid Control ECU
Communication Stop
Mode
"ABS/VSC/TRC" is not displayed on the
"Communication Bus Check" screen of the
intelligent tester
Applies to "Skid Control ...
Settings display
The settings of the following items can be changed, refer to
Language
Select to change the language on the display.
Units
Select to change the unit for measure of the fuel consumption and
outside temperature.
Eco Driving Indicator Light
Select to activate/deactivate the Eco Driving ...
