Toyota Sienna Service Manual: Symptom confirmation and diagnostic trouble code
HINT:
The diagnostic system in the SIENNA has various functions.
- The first function is the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) check. A DTC is a code stored in the ECU memory whenever a malfunction in the signal circuits to the ECU occurs. In a DTC check, a previous malfunction's DTC can be checked by a technician during troubleshooting.
- Another function is the Input Signal Check, which
checks if the signals from various switches are sent to
the ECU correctly.
By using these functions, the problem areas can be narrowed down and troubleshooting is more effective.
Diagnostic functions are incorporated in the following system in the SIENNA.
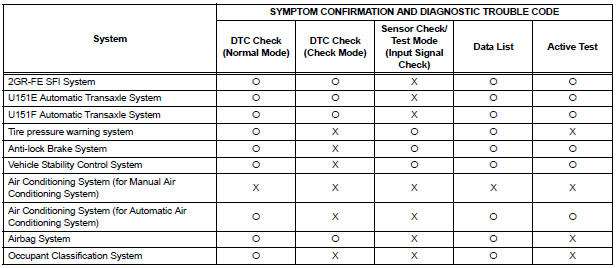
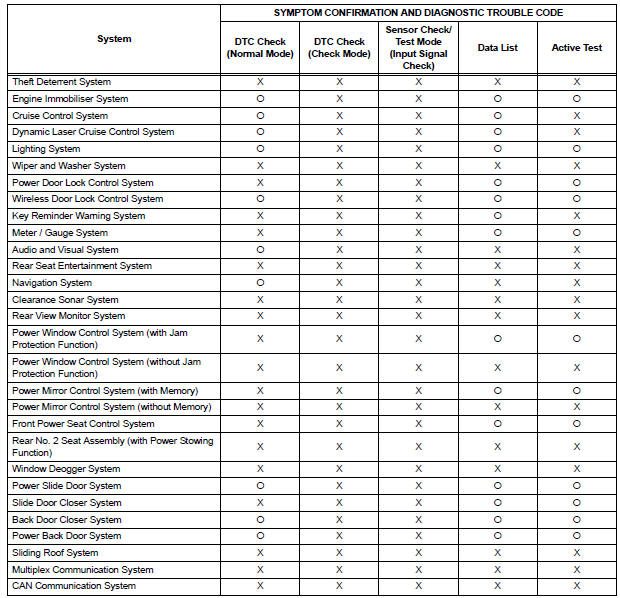
- In the DTC check, it is very important to determine whether the problem indicated by the DTC either: 1) still occurs, or 2) occurred in the past but has returned to normal. In addition, the DTC should be compared to the problem symptom to see if they are related. For this reason, DTCs should be checked before and after confirmation of symptoms (i.e., whether or not problem symptoms exist) to determine current system conditions, as shown in the flowchart below.
- Never skip the DTC check. Failing to check DTCs may, depending on the case, result in unnecessary troubleshooting for systems operating normally or lead to repairs not related to the problem. Follow the procedures listed in the flowchart in the correct order.
- The following flowchart shows how to proceed with troubleshooting using the DTC check. Directions from the flowchart will indicate how to proceed either to DTC troubleshooting or to the troubleshooting of each problem symptom.
- DTC CHECK

- MAKE A NOTE OF DTCS DISPLAYED AND THEN CLEAR MEMORY

- SYMPTOM CONFIRMATION
Result 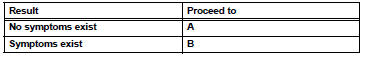


- SIMULATION TEST USING SYMPTOM SIMULATION METHODS

- DTC CHECK
Result 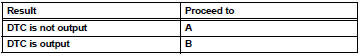


- SYMPTOM CONFIRMATION
Result 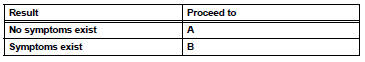
If a DTC was displayed in the initial DTC check, the problem may have occurred in a wire harness or connector in that circuit in the past. Check the wire harness and connectors.


| TROUBLESHOOTING OF EACH PROBLEM SYMPTOM |
The problem still occurs in a place other than the diagnostic circuit (the DTC displayed first is either for a past problem or a secondary problem).
 Customer problem analysis
Customer problem analysis
HINT:
In troubleshooting, confirm that the problem symptoms
have been accurately identified. Preconceptions should be
discarded in order to make an accurate judgment. To
clearly understand w ...
 Symptom simulation
Symptom simulation
HINT:
The most difficult case in troubleshooting is when no
problem symptoms occur. In such a case, a thorough
problem analysis must be carried out. A simulation of the
same or similar conditions ...
Other materials:
Driving assist systems
To help enhance driving safety and performance, the following
systems operate automatically in response to various driving
situations. Be aware, however, that these systems are supplementary
and should not be relied upon too heavily when operating
the vehicle.
ABS (Anti-lock Brake System)
Help ...
On-vehicle inspection
1. INSPECT REAR AIRBAG SENSOR (VEHICLE NOT
INVOLVED IN COLLISION)
Perform a diagnostic system check.
2. INSPECT REAR AIRBAG SENSOR (VEHICLE
INVOLVED IN COLLISION AND AIRBAG HAS NOT
DEPLOYED)
Perform a diagnostic system check.
When the quarter panel of the vehicle or ...
Manual headlight leveling dial (vehicles with discharge headlights)
The level of the headlight aim can be adjusted according to the number
of passengers and the loading condition of the vehicle.
Raises the level of the headlights
Lowers the level of the headlights
Guide to dial settings
Daytime running light system (if equipped)
Bulb type: To ...
