Toyota Sienna Service Manual: Identification of noise source
1. Radio Description
- Radio frequency band
- Radio broadcasts use the radio frequency bands shown in the table below.
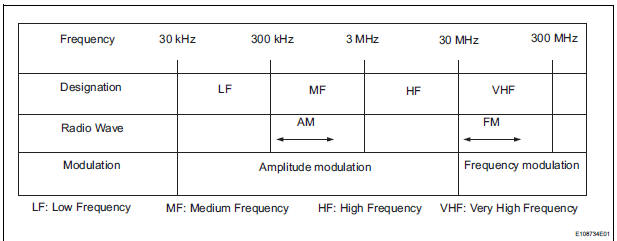
- Service area
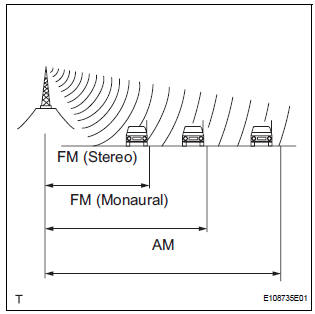
- The service areas of AM and FM broadcasts are vastly different. Sometimes an AM broadcast can be received very clearly but an FM stereo cannot. FM stereo has the smallest service area, and is prone to pick up static and other types of interference such as noise.
- Radio reception problems
HINT: In addition to static, other problems such as "phasing", "multipath", and "fade out" exist. These problems are not caused by electrical noise, but by the radio signal propagation method itself.
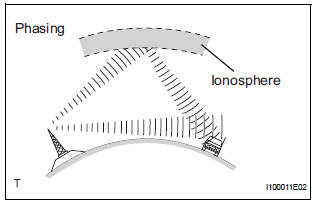
- Phasing
AM broadcasts are susceptible to electrical interference and another kind of interference called phasing. Occurring only at night, phasing is the interference created when a vehicle receives 2 radio wave signals from the same transmitter. One signal is reflected off the ionosphere and the other signal is received directly from the transmitter
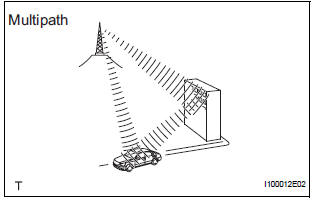
- Multipath
Multipath is a type of interference created when a vehicle receives 2 radio wave signals from the same transmitter. One signal is reflected off buildings or mountains and the other signal is received directly from the transmitter.
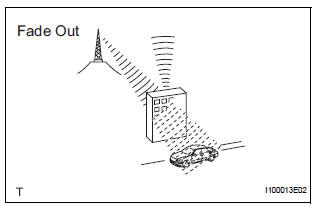
- Fade out
Fade out is caused by objects (buildings, mountains, and other such large obstacles) that deflect away part of a signal, resulting in a weaker signal when the object is between the transmitter and vehicle. High frequency radio waves, such as FM broadcasts, are easily deflected by obstructions. Low frequency radio waves, such as AM broadcasts, are much more difficult to deflect.
- Noise problem
Technicians must have a clear understanding about each customer's noise complaint. Use the following table to diagnose noise problems.
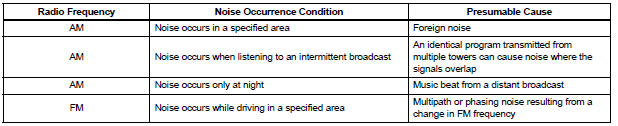
HINT: If the noise does not match the examples above, refer to the descriptions about phasing and multipath.
 How to proceed with
troubleshooting
How to proceed with
troubleshooting
1 VEHICLE BROUGHT TO WORKSHOP
2 INSPECT BATTERY VOLTAGE
Standard voltage:
11 to 14 V
If the voltage is below 11 V, recharge or replace the battery
before proceeding.
3 BASIC INSPECTION
Turn ...
 Problem symptoms table
Problem symptoms table
HINT:
Before inspecting the suspected areas listed in the table
below, check the fuse and relay.
Before inspecting the suspected areas listed in the table
below, check for DTCs.
...
Other materials:
Steering Pad Switch Circuit
DESCRIPTION
This circuit sends an operation signal from the steering pad switch to the
radio receiver.
If there is an open in the circuit, the navigation system cannot be operated
using the steering pad switch.
If there is a short in the circuit, the resulting condition is the same as if ...
Displaying a Bluetooth®
device details
You can confirm and change the registered device details.
Bluetooth® device registration status
Display the ŌĆ£Bluetooth* SetupŌĆØ screen.
*: Bluetooth is a registered trademark of Bluetooth SIG, Inc.
Select the device.
Select ŌĆ£Device InfoŌĆØ.
Following screen is displayed:
...
On-vehicle inspection
1. INSPECT REAR AIRBAG SENSOR (VEHICLE NOT
INVOLVED IN COLLISION)
Perform a diagnostic system check.
2. INSPECT REAR AIRBAG SENSOR (VEHICLE
INVOLVED IN COLLISION AND AIRBAG HAS NOT
DEPLOYED)
Perform a diagnostic system check.
When the quarter panel of the vehicle or ...
