Toyota Sienna Service Manual: Pressure Control Solenoid "C" Performance (Shift Solenoid Valve SL3)
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The ECM uses signals from the vehicle speed sensor to detect the actual gear position (1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th or 5th gear).
Then the ECM compares the actual gear with the shift schedule in the ECM memory
to detect mechanical
troubles of the shift solenoid valves and valve body.
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The ECM commands gear shifts by turning the shift solenoid valves "ON/OFF". According to the input shaft revolution, intermediate (counter) shaft revolution and output shaft revolution, the ECM detects the actual gear position (1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th or 5th gear position). When the gear position commanded by the ECM and the actual gear position are not the same, the ECM illuminates the MIL and stores the DTC.
MONITOR STRATEGY
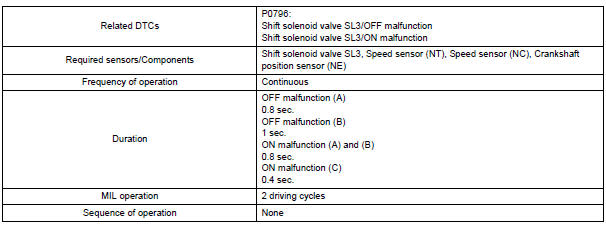
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
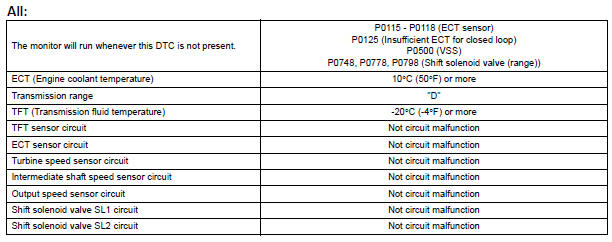

TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
Either of the following conditions is met: OFF malfunction (A) and (B), or ON malfunctions (A), (B) and (C) 2 detections are necessary per driving cycle: 1st detection; temporary flag ON 2nd detection; pending fault code ON

INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT: Using the intelligent tester to perform ACTIVE TEST allows relays, VSVs, actuators and other items to be operated without removing any parts. This non-intrusive functional inspection can be very useful because intermittent operation may be discovered before parts or wiring is disturbed. Performing ACTIVE TEST early in troubleshooting is one way to save diagnostic time. DATA LIST information can be displayed while performing ACTIVE TEST.
1. PERFORM ACTIVE TEST
(a) Warm up the engine.
(b) Turn the ignition switch off.
(c) Connect the intelligent tester together with the CAN VIM (controller area network vehicle interface module) to the DLC3.
(d) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(e) Turn on the tester.
(f) Select the item "DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED OBD II / ACTIVE TEST / SHIFT".
(g) According to the display on the tester, perform the "ACTIVE TEST".
HINT: While driving, the shift position can be forcibly changed with the intelligent tester.
Comparing the shift position commanded by the ACTIVE TEST with the actual shift
position enables you
to confirm the problem (See page AX-30).
HINT:
- This test can be conducted when the vehicle speed is 50 km/h (31 mph) or less.
- The shift position commanded by the ECM is shown in the DATA LIST/SHIFT display on the intelligent tester.
1 CHECK OTHER DTCS OUTPUT (IN ADDITION TO DTC P0796)
(a) Connect the intelligent tester together with the CAN VIM (controller area network vehicle interface module) to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position and turn the OBD II scan tool or the intelligent tester main switch ON.
(c) When you use intelligent tester: Select the item "DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED OBD II / DTC INFO / CURRENT CODES".
(d) Read the DTCs using the OBD II scan tool or the intelligent tester.
Result 
HINT: If any other codes besides "P0796" are output, perform the troubleshooting for those DTCs first.

2 INSPECT SHIFT SOLENOID VALVE SL3
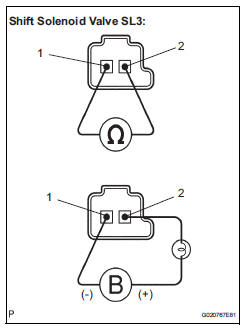
(a) Remove the shift solenoid valve SL3.
(b) Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
Standard resistance
(c) Connect the positive (+) lead with a 21 W bulb to terminal 2 and the negative (-) lead to terminal 1 of the solenoid valve connector, then check the movement of the valve.
OK: The solenoid makes an operating sound.

3 INSPECT TRANSMISSION VALVE BODY ASSEMBLY
OK: There are no foreign objects on each valve and they operate smoothly.


4 INSPECT TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
OK: The torque converter clutch operates normally.


REPAIR OR REPLACE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE ASSEMBLY
 Intermediate Shaft Speed Sensor "A"
Intermediate Shaft Speed Sensor "A"
DESCRIPTION
This sensor detects the rotation speed of the counter gear. By comparing the
counter gear speed signal
(NC) with the direct clutch speed sensor signal (NT), the ECM detects the shift
...
 Pressure Control Solenoid "C" Electrical (Shift
Solenoid Valve SL3)
Pressure Control Solenoid "C" Electrical (Shift
Solenoid Valve SL3)
DESCRIPTION
Shifting from 1st to 5th is performed in combination with "ON" and "OFF"
operation of the shift solenoid
valves SL1, SL2, SL3, S4 and SR which are controlled by the ...
Other materials:
Clock setting
Display the “General Settings” screen.
Operations up to this point can also be performed by select the clock
display
at the top of most screens.
Select the items to be set.
Manual clock setting
Set minutes to 00
The 24-hour time format can
be to on/off.
Select â ...
Installation
1. INSTALL FRONT SEAT ASSEMBLY LH
Place the seat assembly in the cabin.
NOTICE:
Be careful not to damage the body.
Connect the connectors under the seat assembly.
Tighten the 2 bolts on the front side of the seat
assembly.
Torque: 37 N*m (375 kgf*cm, 27 ft.*lb ...
Tachometer Malfunction
DESCRIPTION
The meter CPU receives the engine revolution signal from the ECM via the
direct lines. The meter CPU
displays engine revolution data that is calculated based on the data received
from the ECM.
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
1 PERFORM ACTIVE TEST BY INTELLIGENT TESTER
...
