Toyota Sienna Service Manual: Crankshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit
DTC P0335 Crankshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit
DTC P0339 Crankshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit Intermittent
DESCRIPTION
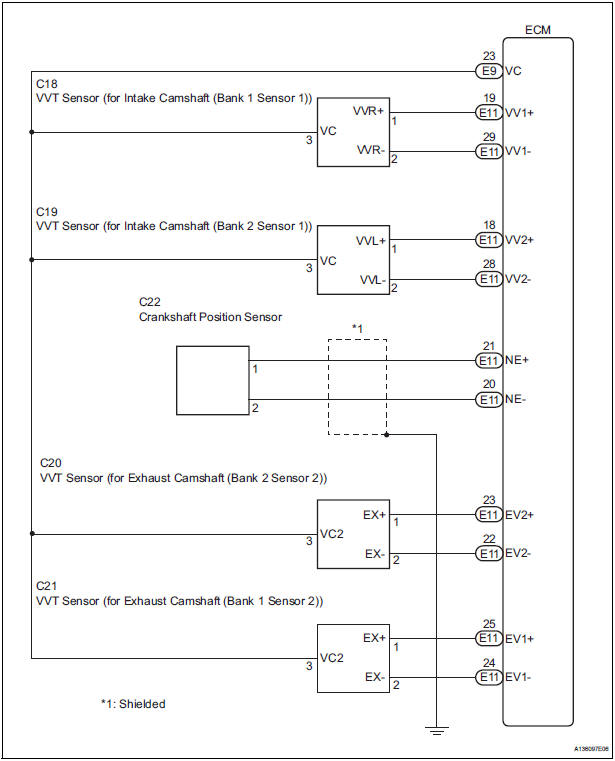
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor system consists of a CKP sensor plate and a pickup coil. The sensor plate has 34 teeth and is installed on the crankshaft. The pickup coil is made of an iron core and a magnet.
The sensor plate rotates as each tooth passes through the pickup coil, and a pulse signal is created. The pickup coil generates 34 signals per engine revolution. Based on these signals, the ECM calculates the crankshaft position and engine RPM. Using these calculations, the fuel injection time and ignition timing are controlled.
|
DTC No. |
DTC Detection Condition |
Trouble Area |
| P0335 |
|
|
| P0339 | Under conditions (a), (b) and (c), no CKP sensor signal
to ECM for 0.05 seconds or more (1 trip detection
logic):
|
|
Reference: Inspection using an oscilloscope
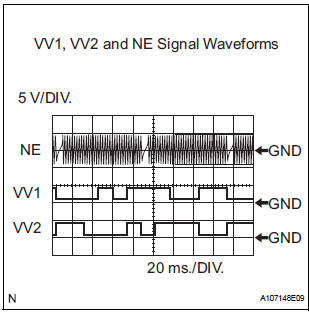
HINT:
- The correct waveform is shown in the illustration.
- VV1+ and VV2+ stand for the VVT sensor signal, and NE+ stands for the CKP sensor signal.
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
If there is no signal from the CKP sensor despite the engine revolving, the ECM interprets this as a malfunction of the sensor.
If the malfunction is not repaired successfully, a DTC is set 10 seconds after the engine is next started.
MONITOR STRATEGY
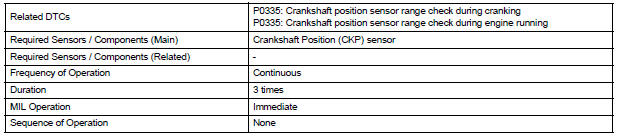
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
All:

Crankshaft Position Sensor Range Check during Cranking P0335:

Crankshaft Position Sensor Range Check during Engine Running P0335:

TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
Crankshaft Position Sensor Range Check during Cranking P0335:
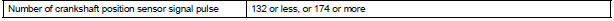
Crankshaft Position Sensor Range Check during Engine Running P0335:

COMPONENT OPERATING RANGE

WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
- If no problem is found by this diagnostic troubleshooting procedure, troubleshoot the engine mechanical systems.
- Check the engine speed. The engine speed can be checked by using the intelligent tester. Perform the following procedure:
- Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
- Start the engine.
- Turn the tester on.
- Select the following menu items: DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED OBD II / DATA LIST / PRIMARY / ENGINE SPD.
The engine speed may be indicated as zero despite the engine revolving normally. This is caused by a lack of NE signals from the Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor. Alternatively, the engine speed may be indicated as lower than the actual engine speed, if the CKP sensor voltage output is insufficient.
- Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. The ECM records vehicle and driving condition information as freeze frame data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can be helpful in determining whether the vehicle was running or stopped, whether the engine was warmed up or not, whether the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, as well as other data recorded at the time of a malfunction.
1 INSPECT CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (RESISTANCE)
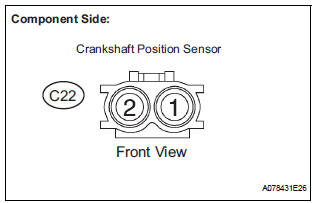
- Disconnect the C22 Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor connector.
- Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
Standard resistance

HINT: Terms "cold" and "hot" refer to the temperature of the coils. "Cold" means approximately -10 to 50C (14 to 122F). "Hot" means approximately 50 to 100C (122 to 212F).
- Reconnect the CKP sensor connector.
2 CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR - ECM)
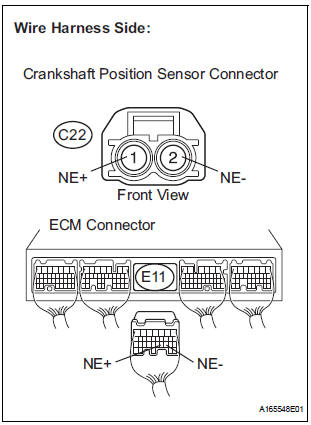
- Disconnect the C22 CKP sensor connector.
- Disconnect the E11 ECM connector.
- Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
Standard resistance : Check for open

Check for short

- Reconnect the ECM connector.
- Reconnect the CKP sensor connector.
3 CHECK SENSOR INSTALLATION (CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR)
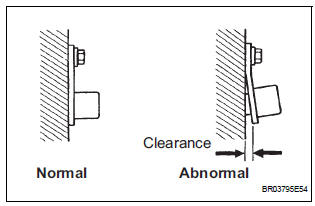
- Check the CKP sensor installation condition.
OK: Sensor is installed correctly.
4 CHECK CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR PLATE (TEETH OF SENSOR PLATE)
- Check the teeth of the sensor plate.
OK: Sensor plate does not have any cracks or deformation
REPLACE ECM
 Knock Sensor Circuit Low Input/ Knock Sensor Circuit High Input
Knock Sensor Circuit Low Input/ Knock Sensor Circuit High Input
DTC P0327 Knock Sensor 1 Circuit Low Input (Bank 1 or
Single Sensor)
DTC P0328 Knock Sensor 1 Circuit High Input (Bank 1 or
Single Sensor)
DTC P0332 Knock Sensor 2 Circuit Low Input (Bank 2)
DTC ...
 Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit
Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit
DTC P0340 Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit (Bank 1
or Single Sensor)
DTC P0342 Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit Low
Input (Bank 1 or Single Sensor)
DTC P0343 Camshaft P ...
Other materials:
Terminals of ECU
1. CHECK OUTER MIRROR CONTROL ECU LH
Disconnect the O9 and O10 connectors.
Measure the voltage and resistance according to
the value(s) in the table below.
Voltage
Resistance
If the result is not as specified, there may be a
malfunction on the wire harness side.
Recon ...
Short to GND in Front Passenger Side Squib
Circuit
DTC B0107/51 Short to GND in Front Passenger Side Squib
Circuit
DESCRIPTION
The front passenger side squib circuit consists of the center airbag sensor
assembly and the front
passenger airbag assembly.
The circuit instructs the SRS to deploy when deployment conditions are met.
DTC B0107/ ...
Removing the second seats
Removing the second outside seats (Tip-up seats)
Pull the armrests up.
Pull the seatback adjustment
lever and fold down the seatback.
The cushion will tip up.
Slide the seat forward to a lock position.
Pull the release lever under
the cushion and simultaneously
lift the ...
