Toyota Sienna Service Manual: Knock Sensor Circuit Low Input/ Knock Sensor Circuit High Input
DTC P0327 Knock Sensor 1 Circuit Low Input (Bank 1 or Single Sensor)
DTC P0328 Knock Sensor 1 Circuit High Input (Bank 1 or Single Sensor)
DTC P0332 Knock Sensor 2 Circuit Low Input (Bank 2)
DTC P0333 Knock Sensor 2 Circuit High Input (Bank 2)
DESCRIPTION
A flat type knock sensor (non-resonant type) has a structure that can detect vibrations over a wide band of frequencies: between approximately 6 kHz and 15 kHz.
Knock sensors are fitted onto the engine block to detect engine knocking.
The knock sensor contains a piezoelectric element which generates a voltage when the engine block vibrates due to knocking. Any occurrence of engine knocking can be suppressed by delaying the ignition timing.
|
DTC No. |
DTC Detection Condition |
Trouble Area |
| P0327 P0332 |
Output voltage of knock sensor 1 or 2 is less than 0.5 V (1 trip detection logic) |
|
| P0328 P0333 |
Output voltage of knock sensor 1 or 2 is more than 4.5 V (1 trip detection logic) |
|
HINT: When any of DTCs P0327, P0328, P0332 and P0333 are set, the ECM enters fail-safe mode. During failsafe mode, the ignition timing is delayed to its maximum retardation. Fail-safe mode continues until the ignition switch is turned off.
Reference: Inspection using an oscilloscope
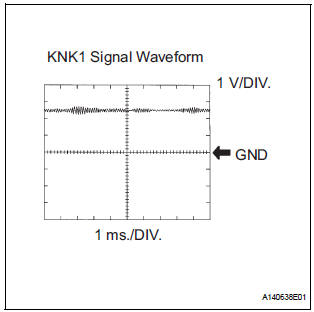
The correct waveform is as shown.
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The knock sensor, located on the cylinder block, detects spark knock. When a spark knock occurs, the piezoelectric element of the sensor vibrates. When the ECM detects a voltage in this frequency range, it retards the ignition timing to suppress the spark knock.
The ECM also senses background engine noise with the knock sensor and uses this noise to check for faults in the sensor. If the knock sensor signal level is too low for more than 10 seconds, or if the knock sensor output voltage is outside the normal range, the ECM interprets this as a fault in the knock sensor and sets a DTC.
MONITOR STRATEGY
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS

TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
Knock Sensor Range Check (Low voltage) P0327 and P0332:

Knock Sensor Range Check (High voltage) P0328 and P0333:

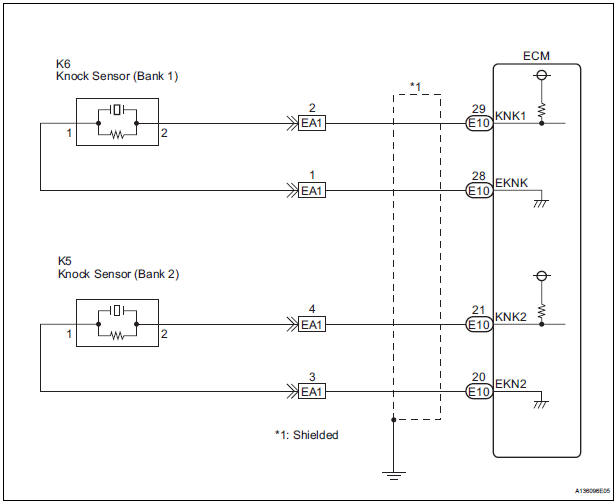
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
- DTCs P0327 and P0328 are for the bank 1 knock sensor circuit.
- DTCs P0332 and P0333 are for the bank 2 knock sensor circuit.
- Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. The ECM records vehicle and driving condition information as freeze frame data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can be helpful in determining whether the vehicle was running or stopped, whether the engine was warmed up or not, whether the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, as well as other data recorded at the time of a malfunction
1 READ VALUE OF DTC OUTPUT (CHECK KNOCK SENSOR CIRCUIT)
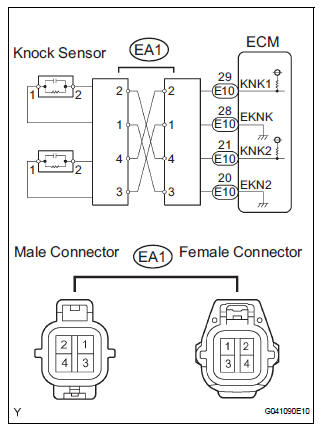
- Disconnect the EA1 connector.
- Using lead wires, connect the connectors as follows.
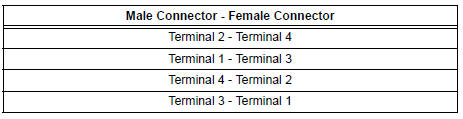
- Warm up the engine.
- Run the engine at 3000 rpm for 10 seconds or more.
- Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
- Turn the ignition switch to the ON position and turn the intelligent tester on.
- Select the items: DIAGNOSIS / ENHANCED OBD II / DTC INFO / CURRENT CODES.
- Read the DTCs.
Result
- Reconnect the EA1 connector.
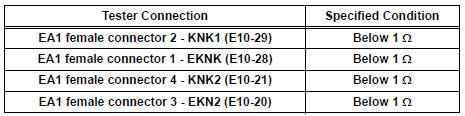
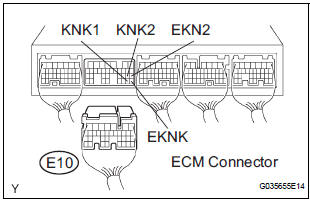
2 CHECK HARNESS OR CONNECTOR (EA1 CONNECTOR - ECM)
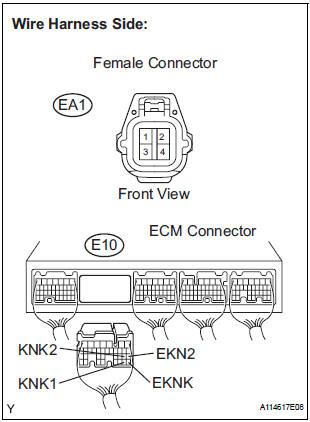
- Disconnect the EA1 connector.
- Disconnect the E10 ECM connector.
- Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
Standard resistance: Check for open
Check for short
- Reconnect the EA1 connector.
- Reconnect the ECM connector.
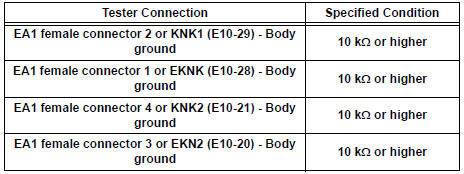
3 INSPECT ECM
- Disconnect the E10 ECM connector.
- Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
- Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the table below.
Standard voltage

- Reconnect the ECM connector.
NOTICE: Fault may be intermittent. Check the wire harness and connectors carefully and retest.
CHECK FOR INTERMITTENT PROBLEMS
4 INSPECT KNOCK SENSOR
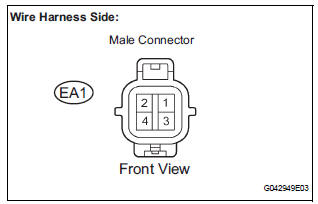
- Disconnect the EA1 connector.
- Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
Standard resistance
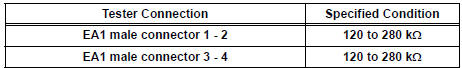
- Reconnect the EA1 connector.
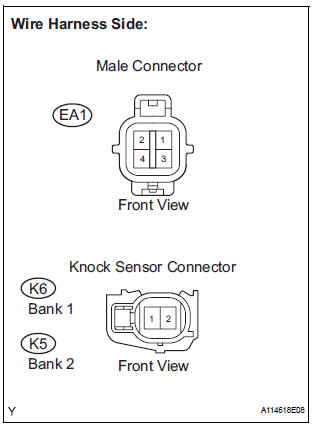
5 CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (EA1 CONNECTOR - KNOCK SENSOR)
HINT:
- If DTC P0327 or P0328 has changed to P0332 or P0333, check the knock sensor circuit on the right bank side.
- If DTC P0332 or P0333 has changed to P0327 or P0328, check the knock sensor circuit on the left bank side.
- Disconnect the EA1 connector.
- Disconnect the K6 and K5 knock sensor connectors.
- Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
Standard resistance: Check for open
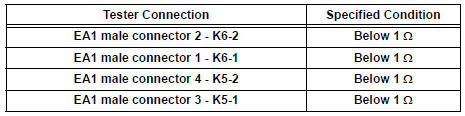
Check for short
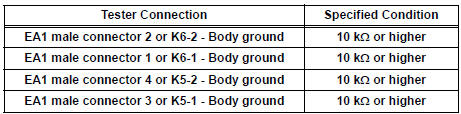
- Reconnect the EA1 connector.
- Reconnect the knock sensor connector.
REPLACE KNOCK SENSOR
 Random / Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected/ Cylinder Misfire Detected
Random / Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected/ Cylinder Misfire Detected
DTC P0300 Random / Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
DTC P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected
DTC P0302 Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected
DTC P0303 Cylinder 3 Misfire Detected
DTC P0304 Cylinder 4 Misfire ...
 Crankshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit
Crankshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit
DTC P0335 Crankshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit
DTC P0339 Crankshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit Intermittent
DESCRIPTION
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor system consists o ...
Other materials:
Lost Communication with Steering Angle Sensor
Module
DTC U0126 Lost Communication with Steering Angle Sensor
Module
DESCRIPTION
This circuit detects the angle and direction of the steering wheel and
automatically transmits a signal to
the skid control ECU and distance control ECU.
DTC No.
DTC Detection Condition
Trouble ...
EVAP System
RELATED DTCS
If any EVAP system DTCs are set, the malfunctioning area can be determined
using the table below.
NOTICE:
If the 0.02 inch reference pressure difference between the first and
second checks is greater than
the specification, the DTCs corresponding to the refe ...
Side Airbag Sensor Assembly RH Circuit Malfunction
DTC B1140/32 Side Airbag Sensor Assembly RH Circuit Malfunction
DESCRIPTION
The side airbag sensor RH circuit consists of the center airbag sensor
assembly and side airbag sensor
RH.
If the center airbag sensor assembly receives signals from the side airbag
sensor RH, it judges whether or
...
